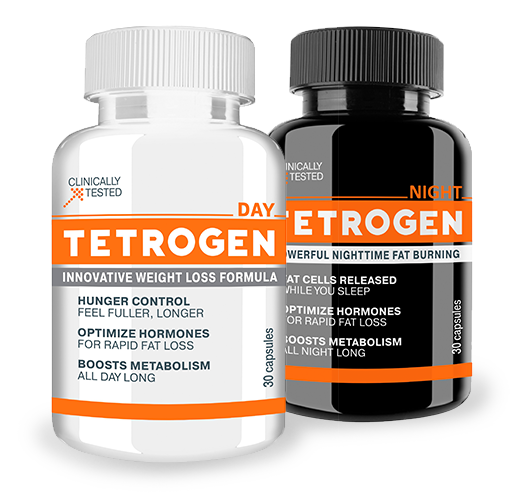
Tetrogen is formulated with all-natural ingredients that reduce inflammation and help reverse leptin resistance for long-term, sustained fat burning.
What Are Anti-Inflammatory Supplements for Weight Loss?

When you read the title of this article “anti-inflammatory supplements for weight loss,” your first thought may have been, “What does inflammation have to do with weight loss?” The short answer is a lot more than you might think.
Before we look at specific supplements, let’s first take a look at inflammation. For example, what is it? And what does it do to the body? Then we can dive into how inflammation affects weight loss and the lifestyle changes that can affect both.
What Is Inflammation and How Does It Impact Weight Loss or Gain?
You’ve probably heard that inflammation is negative and you want to suppress it. It is, after all, the cause of many chronic disease states.
However, inflammation is actually a natural, normal, and vital part of your immune system’s response to injury and infection. The body uses acute inflammation as a signal to the immune system to start the healing and repair process for damaged tissues. It also helps defend against foreign invaders (such as viruses and bacteria). 1
Without the inflammatory response, wounds fester, and even minor infections could become deadly.
Let’s say, for example, that you get a cut on your hand, you sprain your ankle during a hike, or you start coming down with a cold and your throat starts feeling scratchy. The body responds locally with redness, swelling, heat, and depending on the injury, perhaps pain and loss of movement or function. This acute inflammation is caused the by the dilation of blood vessels to increase blood flow, sending in a swarm of white blood cells (a key part of the immune response) to stimulate the healing process.
In addition, other natural healing chemicals like cytokines are sent to the damaged tissues to help bring in more immune cells, hormones, and nutrients. Other hormone-like compounds called prostaglandins can be sent in to create blood clots to heal damaged tissue or trigger heat (i.e., fever) or pain.
Chronic Inflammation and It’s Impact on Weight Gain and Obesity

Issues only arise when the inflammatory process has been prolonged or happens where it’s not needed. This is called chronic inflammation. And it’s why inflammation has such a bad rap.
To begin with, chronic inflammation can last several months to even years. What’s worse is this slow, long-term inflammation has been referred to as “a unifying theory of disease.” 2
In fact, it’s been linked to:
- Coronary artery disease
- Stroke
- Heart disorders
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Diabetes
- Cancer and tumor progression 3
- Alzheimer’s and dementia
- Depression
- Leaky gut syndrome (aka intestinal permeability)
- ALS 4
- Chronic respiratory diseases
- Weight gain and obesity
- Arthritis and joint diseases
- Asthma and allergies
- Lupus
Furthermore, chronic inflammation often runs under the radar. Thus, neither we nor our healthcare practitioners know it’s affecting us. Still, there are some common signs of inflammation to watch for, such as:
- body pain
- fatigue
- brain fog
- insomnia
- depression and anxiety
- gastrointestinal complaints (like constipation, diarrhea, and acid reflux)
- mouth sores and skin issues
- joint pain
- weight gain or loss
- increased belly fat
- and frequent infections
But symptoms can be subtle. In addition, inflammation can often be found from a blood test that indicates a rise in immune system marketers (such as C-reactive protein or CRP). And sometimes, that’s the only indication. Yet even if we aren’t aware of it or don’t have symptoms, chronic inflammation can be causing damage and increasing our risk of disease.
Causes of Chronic Inflammation
The big question then is what causes chronic inflammation? In short, when the body perceives a threat, even if there isn’t an injury or disease to combat, low levels of inflammation can be turned on. Once triggered, the body responds with a flood of white blood cells. Yet now, they don’t have anything to do or anywhere to go. In response, they can sometimes start attacking healthy cells, tissues, or organs.
Researchers are still studying all of the implications, but theories include the buildup of plaque in arteries can increase and prolong inflammation. In response, the body could try to wall off plaque. This could then increase the risk of heart disease or stroke due to lack of blood flow. 5 Doctors have also suggested that chronic inflammation could damage DNA, which could eventually lead to cancer. 6
Other causes of chronic inflammation and resulting weight gain
The failure of the body to eliminate the source of acute inflammation, such as a virus, bacteria, fungi, or other parasite, allowing it to remain in the body for an extended amount of time.
Exposure to a low level of a chemical irritant or foreign material (e.g., silica dust). Any additives and preservatives found in processed foods also increase inflammation.
An autoimmune disorder in which part of the body is seen as a foreign antigen (as seen in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus).
Reoccurring acute inflammation (such as in people who have tuberculosis).
Oxidative stress caused by free radicals, advanced glycation end products (AGEs), uric acid, etc. 1
In addition, there are several risk factors that have been associated with chronic inflammation, including:
- Increasing age
- Obesity or excess weight, especially around the waist/belly
- Diets high in trans fats, saturated fat, and refined sugar, which are associated with pro-inflammatory markers
- Intakes of high amounts of processed meats and processed foods
- Smoking
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Low sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen in men and women
- Stress and the elevation of cortisol levels
- Sleep disorders (e.g., irregular sleep schedules)
- Exposure to chemicals, additives, pesticides, and even pollution
- Contact with phthalates, which are found in numerous skincare and cosmetic products and may be linked to oxidative stress as well as inflammation
- Nutrient deficiencies, especially low levels of vitamins D, B6, and B12.
- Sitting too much or a sedentary lifestyle
Chronic Inflammation and Weight Gain

Researchers have found that obesity leads to low-grade chronic inflammation. 7 And the relationship appears to be linier. That is, as you gain weight, inflammation levels go up. It also goes the other way. That is, inflammation markers are highly associated with obesity. 8
Inflammation appears to affect weight in a number of ways. For instance, when threatened, the body releases cytokines, which turn on the immune response and inflammation. This can interfere with insulin response and lead to or worsen insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body produces enough insulin, but the cells don’t respond as they should, so blood sugar stays high.
This, consequently, can lead to type 2 diabetes and a number of other consequences. Of course, that can include additional weight gain, especially around the belly, and increased inflammation. 9 It can become a vicious cycle as higher inflammation may make it harder to lose weight.
Inflammation has also been shown to interfere with the body’s response to leptin. Leptin is the hormone that tells the body when it’s had enough to eat or has enough body fat stored. And if it isn’t functioning well, you may get hunger signals when you shouldn’t, causing you to overeat. In fact, leptin-resistance is now believed to be a major driver in weight gain.
Losing weight, on the other hand, has been linked to decreased inflammation, 10 especially if weight loss of at least 10% is achieved. 11
Can We Fight Inflammation to Reduce Weight?

If you are suffering from chronic inflammation, there is something you can do about it. Both dietary and lifestyle changes can help remove triggers. According to research, the most effective way to decrease chronic inflammation is to lose weight if you are currently overweight.
Fortunately, many of the methods to help reduce inflammation may also likely help you lose weight. To help manage inflammation, research recommends:

Limiting the consumption of sodas, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars. 12
Avoiding artificial sweeteners and other artificial food additives.
Reducing the intake of trans fats and refined vegetable oils
Consuming plenty of fruits and vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, blueberries, and apples, which are all high in antioxidants and polyphenols and other anti-inflammatory compounds.

Eating more fiber, which may help lower levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha.
Consuming nuts and seeds regularly.
Watching the ratio between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the diet. Most people take in too much omega-6 while not getting nearly enough omega-3 fatty acids. Avoid foods with refined vegetable oils (as found in snack foods, crackers, cookies, and other baked goods), and consume more omega-3-rich foods like salmon, sardines, mackerel, flax and chia seeds, avocados, and walnuts.
In other words, ensure you’re eating a mostly whole-food, nutrient-rich diet, such as the Mediterranean Diet. 13, 14, 15
Other Ways to Reduce Inflammation and Lose Weight

Adding green and black tea polyphenols to the diet, as the polyphenols in tea are associated with reducing CRP.Consuming curcumin, which is found in turmeric. Curcumin has been associated with improvements in several inflammatory conditions.
Eating a nutrient-rich diet that supplies the necessary micronutrients like magnesium, vitamin D, B vitamins, vitamin E, zinc, and selenium.

Flavoring foods with turmeric, garlic, cinnamon, cayenne pepper, ginger, and other herbs and spices.
Managing stress levels.
If you are looking to indulge, try 70 to 85% dark chocolate, which provides several minerals as well as flavanols. Choose a high-quality, low-sugar option from brands like Endangered Species, Alter Eco, Ghirardelli, Taza, Pure7, or Theo.
Ensuring you’re getting good quality sleep. One study found that folks who got less than eight hours of sleep per night had a higher risk of gaining weight. 16

Burning additional energy by incorporating regular moderate exercise into your daily routines.
Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. (Keep a reusable bottle of water with you to sip from all day long.)
Using Anti-Inflammatory Supplements for Weight Loss
Several drugs are used regularly to help combat chronic inflammation. These include metformin, statins, non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin), and corticosteroids. 1, 17 More recently, cannabinoids are being examined for their potential role in immunoregulation. 18, 19
While no supplement can diagnose, treat, or prevent a disease, there are some supplements that have been shown in research to also support the body’s ability to fight the effects of chronic inflammation.
Some of the top anti-inflammatory supplements for weight loss include:

Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): This antioxidant supplement may help protect cells from damage as well as help restore levels of key antioxidants like C and E. 20 It’s also been shown to reduce blood levels of inflammatory markers like IL-6 and ICAM-1 at 300 to 600 mg daily.
Curcumin: Found in the popular spice turmeric, curcumin provides numerous health benefits, including decreased inflammation. 21 It may be especially effective when combined with piperine from black pepper, which can increase its absorption by up to 2,000%. 22 Recommended amounts are 100 to 500 mg daily.

Fish Oil: As mentioned above, fish oil and the omega-3 fatty acids they contain have been found to decrease inflammation associated with a number of conditions. If fish isn’t your favorite food, consider supplementing with 1 to 1.5 grams of omega-3s from EPA and DHA per day. It is not, however, recommended for people on blood thinners or who take aspirin unless suggested by your doctor.
Are There Anti-inflammatory Supplements for Weight Loss?
Beyond looking at supplements that may support the body’s fight against inflammation, it’s also worth looking at those that can help one of the most prevalent causes of inflammation: weight gain and obesity.
There are key ingredients to look for in what are commonly referred to as “anti-inflammatory supplements for weight loss.” (Again, no supplement can diagnose, treat, or prevent a disease, so supplements are really about supporting the body’s natural ability to respond correctly to inflammation.)
Also Look for Weight Loss Supplements with the Following Anti-Inflammatory Ingredients
Irvingia gabonensis or African Mango (or the patented IGOB131™), which has been found to address central obesity and the associated markers of metabolic syndrome, such as high blood glucose levels, LDL cholesterol, and C-reactive protein. 23 It’s been found to help support weight loss by targeting central (abdominal) obesity and reducing leptin resistance. 24
Dyglomera (or the patented DYG-400) comes from a popular spice found in the jungles of Cameroon. This powerful antioxidant has been found to help the body use sugar for energy more efficiently, so it isn’t stored as fat. Researchers have also reported that “Dyglomera®, the aqueous extract of DG, has anti-inflammatory properties, and is effective in reducing cardiovascular disease risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome in obese human subjects.” 25
The polyphenols found in Green Tea Extract have long been known as potent antioxidants. Now, researchers are finding possible additional benefits, including its ability to help decrease the response to inflammation. As such, green tea may support weight loss as well as address metabolic syndrome and obesity. 26
Melatonin Can Also Help Reduce Inflammation Indirectly
Another popular supplement is melatonin. It’s most well-known for its ability to help people get a good night’s sleep. In addition, research suggests it can help control cravings and support weight loss. Melatonin, however, is also a powerful antioxidant that may help reduce inflammation as well as reduce the destruction of inflammation in the body. 27
All three of these “anti-inflammatory supplements for weight loss” can be found in the Tetrogen® formula in the research-recommended amounts. To learn more about the full formula, read testimonials, and find the research on other key ingredients, visit TetrogenUSA.com.
Remember, inflammation isn’t a bad thing. It’s a necessary and very beneficial natural process to help our bodies heal and recover. It can, unfortunately, get out of hand, though. If inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to weight gain and a number of scary consequences.
If you think you are dealing with chronic inflammation, the first stop should be to your personal health-care practitioner. In addition, there are a number of healthy lifestyle changes you can start to incorporate into your daily routine. These include regular exercise and a nutrient-rich whole-food diet. Finally, it may be worth considering supplements to help your body address chronic inflammation.
Want to Save 15% Off Tetrogen Day and Night That Reduces Inflammation 24 Hours a Day? Then Click Here and Use Promo Code GET15TODAY for 15% Savings!
References:
1 Pahwa R, Jialal I. Chronic inflammation. Chronic Inflammation – ncbi
2 Inflammation: A unifying theory of disease [Internet]. Harvard Health. 2006 [cited 11 May 2020]. Available from: Understanding acute and chronic inflammation – Harvard Health
3 Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer – ncbi. Nature. 2002 Dec;420(6917):860-7.
4 Hunter P. The inflammation theory of disease – ncbi. EMBO Reports. 2012 Nov 1;13(11):968-70.
Additional References
5 Inflammation and Heart Disease [Internet]. www.heart.org. 2015 [cited 11 May 2020]. Available from: Inflammation and Heart Disease – American Heart Association
6 Risk Factors: Chronic Inflammation [Internet]. National Cancer Institute. 2015 [cited 11 May 2020]. Available from: Risk Factors: Chronic Inflammation – National Cancer Institute
7 Castro AM, Macedo-de la Concha LE, Pantoja-Meléndez CA. . Revista Médica del Hospital General de México. 2017 Apr 1;80(2):101-5.
8 Tuomisto K, Jousilahti P, Havulinna AS, Borodulin K, Männistö S, Salomaa V. Role of inflammation markers in the prediction of weight gain and development of obesity in adults – ScienceDirect – A prospective study. Metabolism Open. 2019 Sep 1;3:100016.
Additional References
9 Hardy OT, Czech MP, Corvera S. What causes the insulin resistance underlying obesity? – ncbi. Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Obesity. 2012 Apr;19(2):81.
10 Nicklas BJ, Ambrosius W, Messier SP, Miller GD, Penninx BW, Loeser RF, Palla S, Bleecker E, Pahor M. Diet-induced weight loss, exercise, and chronic inflammation in older, obese adults: a randomized controlled clinical trial – PubMed. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2004 Apr 1;79(4):544-51.
11 Forsythe LK, Wallace JM, Livingstone MB. Obesity and inflammation: the effects of weight loss – PubMed. Nutrition Research Reviews. 2008 Dec;21(2):117-33.
Additional References
12 Aeberli I, Gerber PA, Hochuli M, Kohler S, Haile SR, Gouni-Berthold I, Berthold HK, Spinas GA, Berneis K. Low to moderate sugar-sweetened beverage consumption impairs glucose and lipid metabolism and promotes inflammation in healthy young men: a randomized controlled trial – PubMed. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2011 Aug 1;94(2):479-85.
13 Oliviero F, Spinella P, Fiocco U, Ramonda R, Sfriso P, Punzi L. How the Mediterranean diet and some of its components modulate inflammatory pathways in arthritis – PubMed. Swiss Medical Weekly. 2015 Nov 2;145(4546).
Additional References
14 Koloverou E, Panagiotakos DB, Pitsavos C, Chrysohoou C, Georgousopoulou EN, Grekas A, Christou A, Chatzigeorgiou M, Skoumas I, Tousoulis D, Stefanadis C. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and 10-year incidence (2002-2012) of diabetes: correlations with inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers in the ATTICA cohort study – PubMed. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews. 2016 Jan;32(1):73-81.
15 Casas R, Sacanella E, Urpi-Sarda M, Chiva-Blanch G, Ros E, Martínez-González MA, Covas MI, Lamuela-Raventos RM, Salas-Salvado J, Fiol M, Arós F. The effects of the Mediterranean diet on biomarkers of vascular wall inflammation and plaque vulnerability in subjects with high risk for cardiovascular disease. A randomized trial – PubMed. PloS One. 2014;9(6).
Additional References
16 Patel SR, Hu FB. Short sleep duration and weight gain: A systematic review. Obesity 2008 Mar;16(3):643-53.
Additional References
17 Vane JR, Botting RM. Anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanism of action – SpringerLink. Inflammation Research. 1998 Oct 1;47(2):78-87.
18 Nagarkatti P, Pandey R, Rieder SA, Hegde VL, Nagarkatti M. Cannabinoids as novel anti-inflammatory drugs. Future Medicinal Chemistry. 2009 Oct;1(7):1333-49.
19 Gertsch J, Leonti M, Raduner S, Racz I, Chen JZ, Xie XQ, Altmann KH, Karsak M, Zimmer A. Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2008 Jul 1;105(26):9099-104. Why Cannabis Stems Inflammation – ScienceDaily
Additional References
20 Andrea Moura F, Queiroz de Andrade K, Celia Farias dos Santos J, Oliveira Fonseca Goulart M. Lipoic acid: its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory role and clinical applications – PubMed. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 2015 Mar 1;15(5):458-83.
21 Panahi Y, Hosseini MS, Khalili N, Naimi E, Majeed M, Sahebkar A. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of curcuminoid-piperine combination in subjects with metabolic syndrome: a randomized controlled trial and an updated meta-analysis – PubMed. Clinical Nutrition. 2015 Dec 1;34(6):1101-8.
22 Shoba G, Joy D, Joseph T, Majeed M, Rajendran R, Srinivas PS. Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers – PubMed. Planta medica. 1998 May;64(04):353-6.
23 Méndez-del Villar M, González-Ortiz M, Martínez-Abundis E, Pérez-Rubio KG, Cortez-Navarrete M. Effect of Irvingia gabonensis on metabolic syndrome, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion – Journal of Medicinal Food. Journal of Medicinal Food. 2018 Jun 1;21(6):568-74.
Additional References
24 Ngondi JL, Etoundi BC, Nyangono CB, Mbofung CM, Oben JE. IGOB131, a novel seed extract of the West African plant Irvingia gabonensis, significantly reduces body weight and improves metabolic parameters in overweight humans in a randomized double-blind placebo controlled investigation – SpringerLink. Lipids in Health and Disease. 2009 Dec 1;8(1):7.
25 Kuate D, Etoundi BC, Ngondi JL, Muda W, Oben JE. Anti-inflammatory, anthropometric and lipomodulatory effects Dyglomera® (aqueous extract of Dichrostachys glomerata) in obese patients with metabolic syndrome – Functional Foods in Health and Disease. Functional Foods in Health and Disease. 2013 Nov 18;3(11):416-27.
Additional References
26 Oz HS. Chronic inflammatory diseases and green tea polyphenols. Nutrients. 2017 Jun;9(6):561.
27 Reiter RJ, Calvo JR, Karbownik M, Qi W, Tan DX. Melatonin and its relation to the immune system and inflammation – PubMed. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2000 Jan;917(1):376-86.

Mike Dorfman is BS in Biochemistry from the University of Colorado. Mike’s has worked as a personal trainer for Gold’s Gym and helped many clients achieve their weight-loss and fitness goals.
To health first, weight-loss second. Mike and Tetrogen are here to help you make the transition to the healthier, happier, and thinner you!
SIGN UP NOW FOR YOUR FREE WEEKLY EMAILS!
Get brand-new healthy recipes (easy ones), tips 'n tricks, and more...
Bonus: Get discount coupons for our products on a subscription!
You will receive one tip per week. You can unsubscribe at any time. We will never share your information with third parties.